|
To discern the value and quality of the diamonds, jewelers verify each of the 4 Cs - carat weight, cut, clarity, and color. All of these qualities are combined to determine the value of all diamonds. The rarest stones exhibit the finest qualities in each of the 4 Cs and have the most value.
Each of the 4 Cs must be considered to boast a well-balanced diamond. All diamonds have a unique combination of the 4 Cs varying in quality. Being able to identify what makes a particular diamond a right choice will not only be of value to you, but will demonstrate the time and sentiment you've invested on the decision.
Carat:
Carat Weight
All diamonds are measured in carats (not to be confused with Karats, which are used to measure the purity of gold). By definition, 1 carat is exactly 0.20 miligrams. The term points is also used, especially for stones that weight less than 1/2 a carat. For example, a 50 point diamond is the equivalent of a 1/2 carat stone (0.50). Large diamonds, which are found infrequently in nature, flaunt the stone's delicate color and exquisite cut, hence the overall brilliance. Though larger diamonds are highly sought, a diamond of lesser size may have higher clarity and color or a more precise cut and be of equal value.
It is important, also, not to confuse weight with size. Two diamonds with exactly the same size might weight differently. The same can be argued when comparing the carat weight among different stones. Since each mineral has a different density, a 1-carat diamond will have a different volume than, say, a 1-carat sapphire.
Cut:
Most confusion arises when discussing the term "Cut". What is cut? Is it the shape of a diamond (say, round, princess)? Is it how well proportioned the different parts of the stone are? Well, most experts agree it is actually a combination of numerous factors (including the ones aforementioned). Nevertheless, and to make things simpler, we will concentrate on three of the most widely used criteria used to measure a diamond's cut.
Shapes:
Shape refers to the inherent shape of the diamond. Among the most common shapes available on the market are the round cut, the marquise, the pear shape, the oval, the princess cut, the emerald cut, the heart shape and the radiant cut.
Proportions
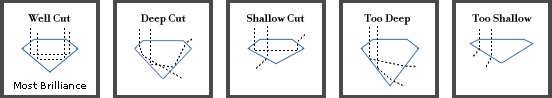
It is in the hands of the master diamond cutter to bring out the scintillating fire of a diamond. Well cut diamonds reflect the maximum amount of light, through the diamond from one mirror- like surface to another, dispersed through the top of the stone. Diamonds cut too shallow or too deep lose light that spills through the side or bottom. Consequently, a poorly proportioned stone is less brilliant and spectacular and accordingly less valuable.
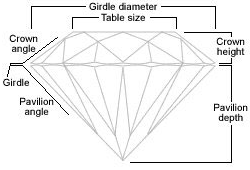
Ideal proportions for a round diamond, for instance, are 59% - 61% Depth (the proportion of the total height of the diamond compared to the girdle diameter) and 53% - 57% Table (the proportion of the table size compared to the girdle diameter). By definition, this is called the "ideal cut" and round diamonds showing these proportions are very expensive and highly sought after.
 |
|
This does not mean, however, that only ideal cut diamonds will show brilliance and fire! There are many other factors to be considered (such as color, clarity and carat size) and any diamond close enough to this measurements will bring the scintillating effect generally sought in a diamond. Use the guide below to get an idea on how to judge the proportions of a diamond for most shapes.
|
| |
Ideal Cut |
Very Good Cut |
Good Cut |
| Depth % |
59% to 61% |
59% to 63% |
63% to 66% |
| Table % |
53% to 57% |
53% to 61% |
62% to 65% |
| |
Ideal Cut |
Very Good Cut |
Good Cut |
| Depth % |
60% to 70% |
56% to 75% |
52% to 78% |
| Lenght / Width Ratio |
2.00:1 to 1.00:1 |
2.25:1 to 1.75:1 |
2.30:1 to 1.70:1 |
| |
Ideal Cut |
Very Good Cut |
Good Cut |
| Depth % |
60% to 70% |
56% to 75% |
52% to 78% |
| Table % |
1.50:1 |
1.60:1 to 1.40:1 |
1.70:1 to 1.35:1 |
| |
Ideal Cut |
Very Good Cut |
Good Cut |
| Depth % |
60% to 70% |
56% to 75% |
52% to 78% |
| Table % |
1.70:1 |
1.70:1 to 1.50:1 |
1.80:1 to 1.40:1 |
| |
Ideal Cut |
Very Good Cut |
Good Cut |
| Depth % |
60% to 70% |
56% to 75% |
52% to 78% |
| Table % |
1.70:1 to 1.50:1 |
1.75:1 to 1.45:1 |
1.80:1 to 1.40:1 |
| |
Ideal Cut |
Very Good Cut |
Good Cut |
| Depth % |
60% to 70% |
56% to 75% |
52% to 78% |
| Table % |
1.80:1 to 1.45:1 |
1.80:1 to 1.60:1 |
2.00:1 to 1.00:1 |
| |
Ideal Cut |
Very Good Cut |
Good Cut |
| Depth % |
60% to 70% |
56% to 75% |
52% to 78% |
| Lenght / Width Ratio |
1.05:1 |
1.10:1 |
1.15:1 |
Clarity:
|
The clarity of a diamond determines how captivating its gleam is. All diamonds have identifying characteristics, but most are invisible to the naked eye. Under the scrutiny of a jeweler's 10X magnifying loupe the appearance of tiny crystals, feathers or clouds can be identified. These natural phenomena are called inclusions. Large inclusions may interfere with the path of light cascading through a diamond, thus effecting its vibrancy. There are five categories in class that anyone interested in purchasing a diamond should be aware of when grading clarity. |
|
 |
FL & IF
Diamonds that reveal no flaws on the surface or internally. These are the rarest and most beautiful gems treasured for their absolute purity.
VVS1 or VVS2
 |
Diamonds with minute inclusions absolutely invisible to the naked eye. Only through careful inspection with a microscope can these tiny inclusions be accurately pinpointed. The brilliance of the stone does not suffer in this |
VS1 or VS2
 |
Diamonds with tiny inclusions difficult to locate. Only a trained eye looking through a 10X loupe can pinpoint the inclusions in this category. The inclusions are nearly impossible to see with the naked eye. |
SI1 - SI3
 Diamonds with inclusions easily identified through a loupe. Finding flaws in this category with the naked eye is difficult for the SI1 - SI2 range. The gems in this category maintain their integrity, depending on the location of the inclusions. They are an attractive choice when working within a fixed budget without sacrificing beauty or value. Inclusions in an SI3 graded diamond may be seen to the unaided eye, although not with substantial ease. Consider an SI3 as a good I1. |
I1 - I3
 |
Diamonds with inclusions which may be seen by the naked eye. The flaws on the I2-I3 range in this category might have some effect on the brilliance of your diamond. |
Important Information about Clarity Enhancement:
|
|
|
There are a few methods used by the diamond industry to enhance the clarity of a diamond. Two of the most widely used methods are laser drilling and fracture filling. In Laser Drilling, a tiny hole is drilled with a laser beam in order to remove dark inclusions from the diamond.
In Fracture Filling, cleavages and fractures that reach the surface of the stone are filled with a high R. I. material that helps disguise these inclusions.
|
We DO NOT use ANY form of clarity enhancement.
We sell only 100% natural diamonds. |
Color
Grades in the color of diamonds range from D-Z, D being truly colorless and of the highest quality. E and F are also graded as colorless while G, H, I and J are near colorless. Diamonds graded K, L, and M will have obvious hints of color and as the scale approaches P you may find subtle changes in hue and tone. The exceptions to the rule are "Fancy" diamonds- in well-highlighted colors that include pink, blue, red, green, and canary yellow. These are particularly rare and highly treasured. To appreciate the quality of a colorless diamond, compare several stones side by side with a jeweler.
|